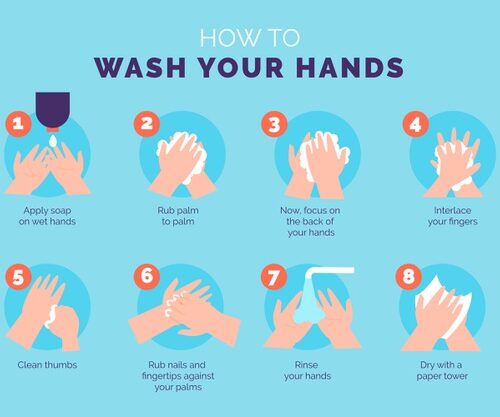
Wash your hands frequently
Regularly and thoroughly clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water.
Why? Washing your hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand rub kills viruses that may be on your hands.
Maintain social distancing
Maintain at least 1 metre (3 feet) distance between yourself and anyone who is coughing or sneezing.
Why? When someone coughs or sneezes they spray small liquid droplets from their nose or mouth which may contain virus. If you are too close, you can breathe in the droplets, including the COVID-19 virus if the person coughing has the disease.

Avoid touching eyes, nose and mouth
Why? Hands touch many surfaces and can pick up viruses. Once contaminated, hands can transfer the virus to your eyes, nose or mouth. From there, the virus can enter your body and can make you sick.

Practice respiratory hygiene
Make sure you, and the people around you, follow good respiratory hygiene. This means covering your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or tissue when you cough or sneeze. Then dispose of the used tissue immediately.
Why? Droplets spread virus. By following good respiratory hygiene you protect the people around you from viruses such as cold, flu and COVID-19.
If you have fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical care early
Stay home if you feel unwell. If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical attention and call in advance.

If you have fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical care early
Stay home if you feel unwell. If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical attention and call in advance.
Follow the directions of the Ministry of Health, Kenya and World Health Organization.
Why? They will have the most up to date information on the situation in Kenya, the region and the world. Calling in advance will allow your health care provider to quickly direct you to the right health facility. This will also protect you and help prevent spread of viruses and other infections.
These Ministry of Health – Public Health Emergency Operation Center Hotline numbers are operational 24-hours a day: 719, +254729471414, +254732353535, +254748592455, and 0800721316 (Toll free).
Stay informed and follow advice given by the Ministry of Health, Kenya
Stay informed on the latest developments about COVID-19. Follow advice given by Ministry of Health, or world Health Organization on how to protect yourself and others from COVID-19.
Why? They will have the most up to date information on whether COVID-19 is spreading in Kenya, the region and the world. They are best placed to advise on what people should be doing to protect themselves.

What is CoronaVirus
What is Covid-19
What are the most common symptoms of Covid-19
What can i do to protect myself and prevent the spread of the disease?
Protection measures for everyone
Stay aware of the latest information on the COVID-19 outbreak, available on the WHO website and through your national and local public health authority. Many countries around the world have seen cases of COVID-19 and several have seen outbreaks. Authorities in China and some other countries have succeeded in slowing or stopping their outbreaks. However, the situation is unpredictable so check regularly for the latest news.
You can reduce your chances of being infected or spreading COVID-19 by taking some simple precautions:
- Regularly and thoroughly clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water.
Why? Washing your hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand rub kills viruses that may be on your hands. - Maintain at least 1 metre (3 feet) distance between yourself and anyone who is coughing or sneezing.
Why? When someone coughs or sneezes they spray small liquid droplets from their nose or mouth which may contain virus. If you are too close, you can breathe in the droplets, including the COVID-19 virus if the person coughing has the disease. - Avoid touching eyes, nose and mouth.
Why? Hands touch many surfaces and can pick up viruses. Once contaminated, hands can transfer the virus to your eyes, nose or mouth. From there, the virus can enter your body and can make you sick. - Make sure you, and the people around you, follow good respiratory hygiene. This means covering your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or tissue when you cough or sneeze. Then dispose of the used tissue immediately.
Why? Droplets spread virus. By following good respiratory hygiene you protect the people around you from viruses such as cold, flu and COVID-19. - Stay home if you feel unwell. If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical attention and call in advance. Follow the directions of your local health authority.
Why? National and local authorities will have the most up to date information on the situation in your area. Calling in advance will allow your health care provider to quickly direct you to the right health facility. This will also protect you and help prevent spread of viruses and other infections. - Keep up to date on the latest COVID-19 hotspots (cities or local areas where COVID-19 is spreading widely). If possible, avoid traveling to places – especially if you are an older person or have diabetes, heart or lung disease.
Why? You have a higher chance of catching COVID-19 in one of these areas.
Protection measures for persons who are in or have recently visited (past 14 days) areas where COVID-19 is spreading
- Follow the guidance outlined above (Protection measures for everyone)
- Self-isolate by staying at home if you begin to feel unwell, even with mild symptoms such as headache, low grade fever (37.3 C or above) and slight runny nose, until you recover. If it is essential for you to have someone bring you supplies or to go out, e.g. to buy food, then wear a mask to avoid infecting other people.
Why? Avoiding contact with others and visits to medical facilities will allow these facilities to operate more effectively and help protect you and others from possible COVID-19 and other viruses. - If you develop fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical advice promptly as this may be due to a respiratory infection or other serious condition. Call in advance and tell your provider of any recent travel or contact with travelers.
Why? Calling in advance will allow your health care provider to quickly direct you to the right health facility. This will also help to prevent possible spread of COVID-19 and other viruses.
How likely am I to catch Covid-19?
For most people in most locations the risk of catching COVID-19 is still low. However, there are now places around the world (cities or areas) where the disease is spreading. For people living in, or visiting, these areas the risk of catching COVID-19 is higher. Governments and health authorities are taking vigorous action every time a new case of COVID-19 is identified. Be sure to comply with any local restrictions on travel, movement or large gatherings. Cooperating with disease control efforts will reduce your risk of catching or spreading COVID-19.
COVID-19 outbreaks can be contained and transmission stopped, as has been shown in China and some other countries. Unfortunately, new outbreaks can emerge rapidly. It’s important to be aware of the situation where you are or intend to go. WHO publishes daily updates on the COVID-19 situation worldwide.
You can see these at https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports/
How likely am I to catch Covid-19?
For most people in most locations the risk of catching COVID-19 is still low. However, there are now places around the world (cities or areas) where the disease is spreading. For people living in, or visiting, these areas the risk of catching COVID-19 is higher. Governments and health authorities are taking vigorous action every time a new case of COVID-19 is identified. Be sure to comply with any local restrictions on travel, movement or large gatherings. Cooperating with disease control efforts will reduce your risk of catching or spreading COVID-19.
COVID-19 outbreaks can be contained and transmission stopped, as has been shown in China and some other countries. Unfortunately, new outbreaks can emerge rapidly. It’s important to be aware of the situation where you are or intend to go. WHO publishes daily updates on the COVID-19 situation worldwide.
You can see these at https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports/
COVID-19 virus can be transmitted in areas with hot and humid climates
From the evidence so far, the COVID-19 virus can be transmitted in ALL AREAS, including areas with hot and humid weather. Regardless of climate, adopt protective measures if you live in, or travel to an area reporting COVID-19. The best way to protect yourself against COVID-19 is by frequently cleaning your hands. By doing this you eliminate viruses that may be on your hands and avoid infection that could occur by then touching your eyes, mouth, and nose.

Cold weather and snow CANNOT kill the new coronavirus.
There is no reason to believe that cold weather can kill the new coronavirus or other diseases. The normal human body temperature remains around 36.5°C to 37°C, regardless of the external temperature or weather. The most effective way to protect yourself against the new coronavirus is by frequently cleaning your hands with alcohol-based hand rub or washing them with soap and water.

Taking a hot bath does not prevent the new coronavirus disease
Taking a hot bath will not prevent you from catching COVID-19. Your normal body temperature remains around 36.5°C to 37°C, regardless of the temperature of your bath or shower. Actually, taking a hot bath with extremely hot water can be harmful, as it can burn you. The best way to protect yourself against COVID-19 is by frequently cleaning your hands. By doing this you eliminate viruses that may be on your hands and avoid infection that could occur by then touching your eyes, mouth, and nose.
The new coronavirus CANNOT be transmitted through mosquito bites.
To date there has been no information nor evidence to suggest that the new coronavirus could be transmitted by mosquitoes. The new coronavirus is a respiratory virus which spreads primarily through droplets generated when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or through droplets of saliva or discharge from the nose. To protect yourself, clean your hands frequently with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water. Also, avoid close contact with anyone who is coughing and sneezing.

Are hand dryers effective in killing the new coronavirus?
No. Hand dryers are not effective in killing the 2019-nCoV. To protect yourself against the new coronavirus, you should frequently clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water. Once your hands are cleaned, you should dry them thoroughly by using paper towels or a warm air dryer.

Can an ultraviolet disinfection lamp kill the new coronavirus?
UV lamps should not be used to sterilize hands or other areas of skin as UV radiation can cause skin irritation.

How effective are thermal scanners in detecting people infected with the new coronavirus?
Thermal scanners are effective in detecting people who have developed a fever (i.e. have a higher than normal body temperature) because of infection with the new coronavirus.
However, they cannot detect people who are infected but are not yet sick with fever. This is because it takes between 2 and 10 days before people who are infected become sick and develop a fever.

Can spraying alcohol or chlorine all over your body kill the new coronavirus?
No. Spraying alcohol or chlorine all over your body will not kill viruses that have already entered your body. Spraying such substances can be harmful to clothes or mucous membranes (i.e. eyes, mouth). Be aware that both alcohol and chlorine can be useful to disinfect surfaces, but they need to be used under appropriate recommendations.

Do vaccines against pneumonia protect you against the new coronavirus?
No. Vaccines against pneumonia, such as pneumococcal vaccine and Haemophilus influenza type B (Hib) vaccine, do not provide protection against the new coronavirus.
The virus is so new and different that it needs its own vaccine. Researchers are trying to develop a vaccine against 2019-nCoV, and WHO is supporting their efforts.
Although these vaccines are not effective against 2019-nCoV, vaccination against respiratory illnesses is highly recommended to protect your health.

Can regularly rinsing your nose with saline help prevent infection with the new coronavirus?
No. There is no evidence that regularly rinsing the nose with saline has protected people from infection with the new coronavirus.
There is some limited evidence that regularly rinsing nose with saline can help people recover more quickly from the common cold. However, regularly rinsing the nose has not been shown to prevent respiratory infections.

Can eating garlic help prevent infection with the new coronavirus?
Garlic is a healthy food that may have some antimicrobial properties. However, there is no evidence from the current outbreak that eating garlic has protected people from the new coronavirus.

Does the new coronavirus affect older people, or are younger people also susceptible?
People of all ages can be infected by the new coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Older people, and people with pre-existing medical conditions (such as asthma, diabetes, heart disease) appear to be more vulnerable to becoming severely ill with the virus.
WHO advises people of all ages to take steps to protect themselves from the virus, for example by following good hand hygiene and good respiratory hygiene.

Are antibiotics effective in preventing and treating the new coronavirus?
No, antibiotics do not work against viruses, only bacteria.
The new coronavirus (2019-nCoV) is a virus and, therefore, antibiotics should not be used as a means of prevention or treatment.
However, if you are hospitalized for the 2019-nCoV, you may receive antibiotics because bacterial co-infection is possible.

Are there any specific medicines to prevent or treat the new coronavirus?
To date, there is no specific medicine recommended to prevent or treat the new coronavirus (2019-nCoV).
However, those infected with the virus should receive appropriate care to relieve and treat symptoms, and those with severe illness should receive optimized supportive care. Some specific treatments are under investigation, and will be tested through clinical trials. WHO is helping to accelerate research and development efforts with a range or partners.



